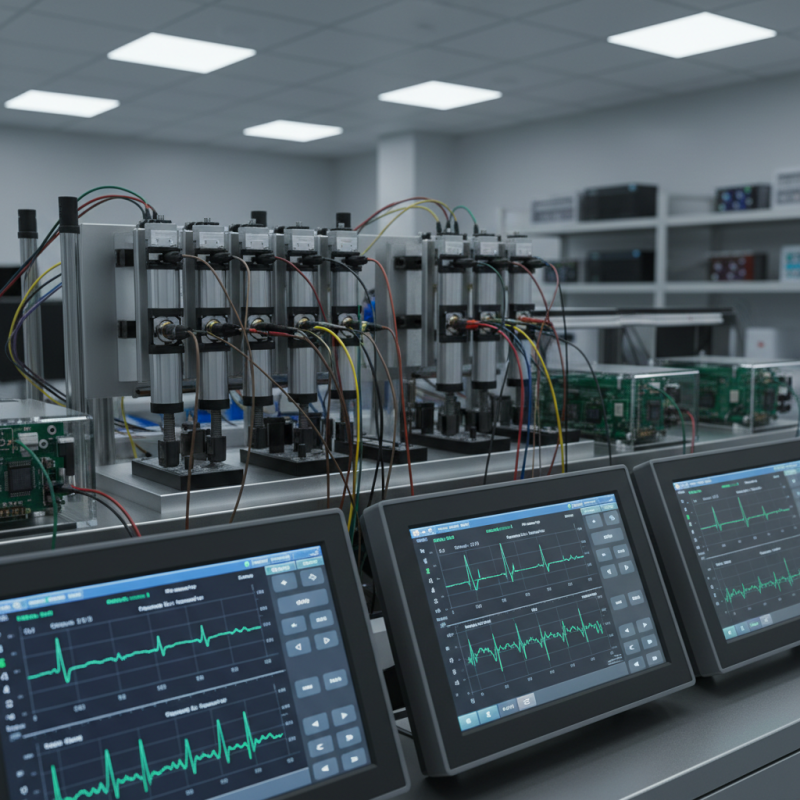
Top 10 Lithium Cell Testers for Accurate Battery Performance Evaluation?
In the realm of energy storage, lithium batteries are essential. Evaluating their performance requires precision. A reliable Lithium Cell Tester can provide critical insights. These testers help measure capacity, resistance, and overall health.
However, not all testers are created equal. The market offers various options, each with unique features. Some may lack accuracy, while others may be overly complex. Consumers need a clear understanding to make informed choices.
Choosing the right Lithium Cell Tester can be challenging. A poor selection can lead to misleading results. How often do users realize the importance of accurate testing? This oversight can lead to wasted resources and ineffective energy solutions. With the right tools, one can truly gauge the potential of lithium cells.
Top Features to Look for in Lithium Cell Testers
When evaluating lithium cell testers, it’s crucial to focus on key features. Accuracy is paramount. Testers should deliver precise voltage readings. Without this precision, testing results can mislead you. Consider testers that offer a wide range of measurement options. Some devices measure capacity, internal resistance, and cycle life. This helps in understanding battery health.
Another important aspect is user-friendliness. A complex interface can lead to errors. Choose testers with intuitive displays. Simple menus can make a significant difference when time is limited. Also, think about portability. Compact designs can be advantageous for field testing. If it’s not easy to carry, it won't be used as often.
Don’t overlook safety features. Lithium batteries can be volatile. Look for testers that include over-voltage and short-circuit protection. While this adds to the cost, it’s a vital investment. Reflect on your specific needs. What applications will you use the tester for? Knowing this can guide your choice.
Top 10 Lithium Cell Testers Performance Comparison
This chart displays the performance evaluation metrics of the top 10 lithium cell testers based on key features such as accuracy, battery capacity range, and measurement speed. Each tester has been rated on a scale from 1 to 10 for the following dimensions:
- Accuracy
- Battery Capacity Range
- Measurement Speed
Understanding Lithium Battery Chemistry for Accurate Testing
Lithium battery chemistry is complex yet fascinating. Understanding its components, like lithium ions and electrolyte solutions, is vital for accurate testing. According to recent industry reports, over 90% of electric vehicles now use lithium-ion technology. This highlights the need for precise performance evaluation tools.
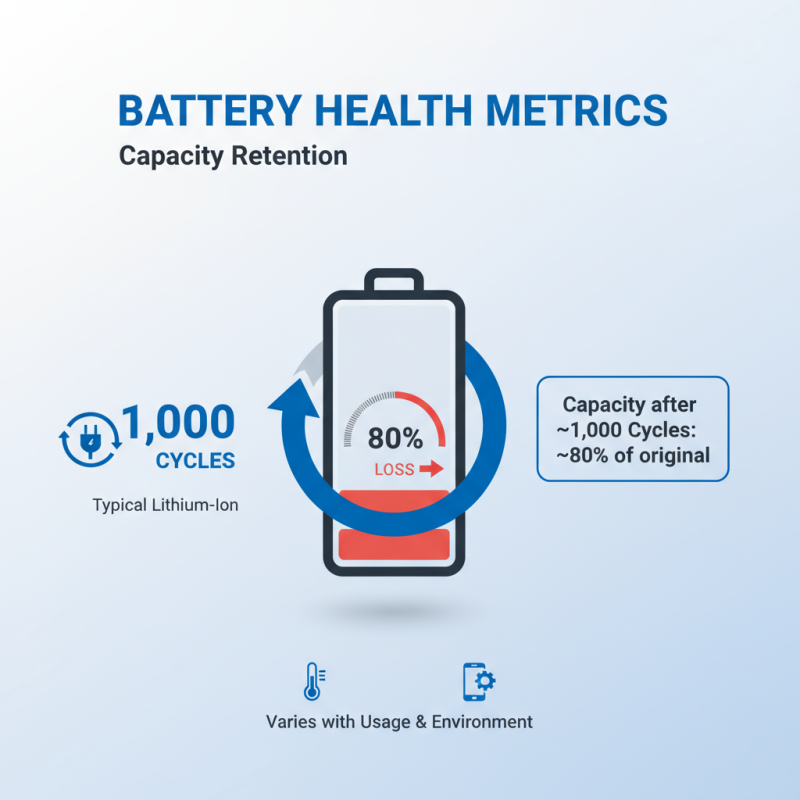
Lithium batteries operate on ion movement between the anode and cathode. Temperature, charge cycles, and aging can significantly impact performance. A study showed that battery capacity diminishes by 20% after over 800 charge cycles. Testing must consider these variables to ensure reliability in real-world applications. This is where accurate lithium cell testers come into play.
Improper testing methods can lead to significant errors. For instance, using outdated equipment may result in miscalculations of battery health. Testing protocols should be regularly updated to match advancements in battery tech. Industry experts emphasize that effective testing is crucial for optimizing battery life and efficiency. Continuous evaluation and adaptation are necessary.
Comparative Analysis of Leading Lithium Cell Testers on the Market
When evaluating lithium cell performance, choosing the right tester is crucial. Many options promise accuracy and reliability, yet they vary significantly in features. A reliable tester should allow for easy monitoring of voltage, capacity, and internal resistance. Key specifications can help guide your choice.
Tips: Always consider the size and weight of the tester. Portable options make for easier field use. Look for models that offer a clear display. This will make reading results quicker and less prone to errors.
Another aspect to remember is calibration. Regularly checking your tester's calibration ensures accurate results. Some testers may require complex procedures for this. If yours does, consider taking a moment to reflect on whether it's the right tool for your needs.
In the realm of battery testing, user-friendly interfaces can change the game. Complicated controls can lead to mistakes or misreadings. Simplicity is often more effective. Be wary of testers that sound too good to be true. Reflect on user feedback and reviews. These insights can inform your decision.
Industry Standards and Certifications for Battery Testing Equipment
In the battery testing industry, industry standards and certifications play a crucial role. They ensure accuracy and reliability in performance evaluation. Organizations like ISO and IEC set benchmarks. Following these standards helps manufacturers achieve quality control.
Recent reports highlight the importance of certified testers. For instance, a study found that 78% of companies that adhere to testing standards see fewer product failures. This statistic highlights the value of using recognized protocols. Many testers now come equipped with features that comply with these regulations. They offer precise measurements of output and durability.
However, not all testing equipment meets these rigorous standards. Some tools fail to provide accurate data. This inconsistency can lead to costly mistakes in production. A careful evaluation of testing equipment is needed. Companies must invest in reliable testers that align with industry certifications.
Top 10 Lithium Cell Testers for Accurate Battery Performance Evaluation
| Model |
Voltage Range (V) |
Current Rating (A) |
Measurement Accuracy (%) |
Standards Compliance |
| Tester A |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 10 |
±0.5 |
ISO 9001, IEC 62133 |
| Tester B |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 5 |
±1.0 |
CE, UL |
| Tester C |
0 - 4.5 |
0 - 20 |
±0.2 |
ISO 17025, RoHS |
| Tester D |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 15 |
±0.5 |
IEC 60950, UL |
| Tester E |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 30 |
±0.3 |
ISO 9001, CE |
| Tester F |
0 - 4.5 |
0 - 10 |
±0.4 |
RoHS, IEC 62133 |
| Tester G |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 25 |
±0.6 |
ISO 17025, CE |
| Tester H |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 12 |
±0.5 |
IEC 60950, UL |
| Tester I |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 8 |
±0.3 |
ISO 9001, RoHS |
| Tester J |
0 - 4.2 |
0 - 22 |
±0.7 |
IEC 62133, UL |

Home
Products
Power Cell Testing System
Digital Battery Testing System
 32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
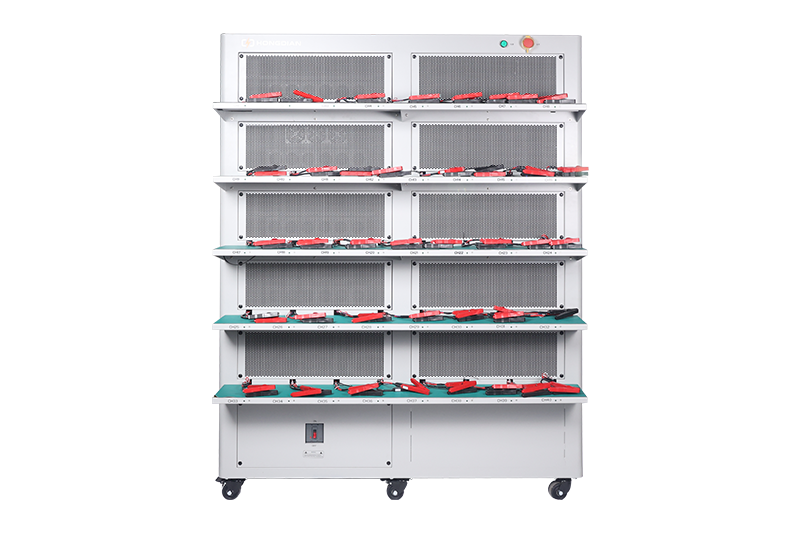 40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
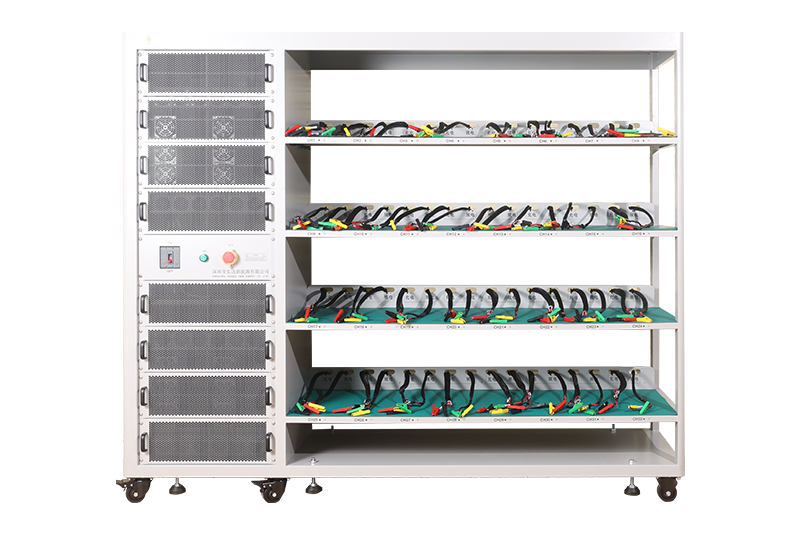 64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
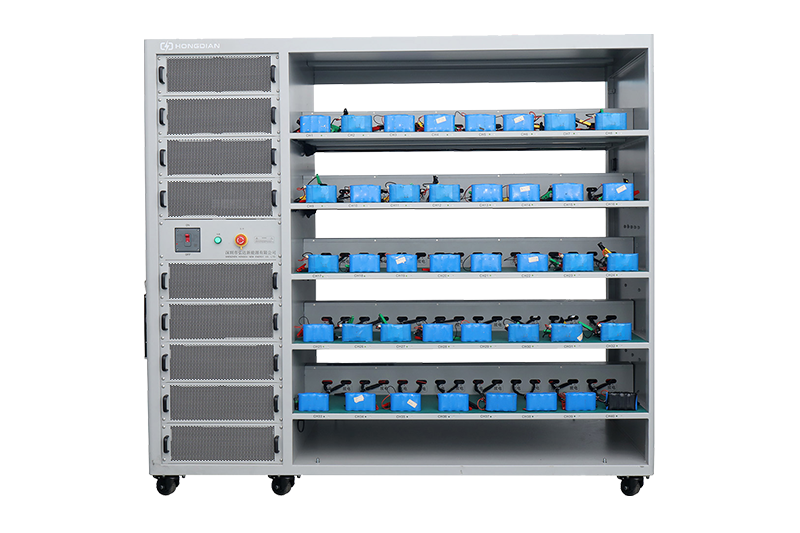 80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
Module Pack Testing System
Developing Portable Battery Testing
About Us
Service
Case&Solution
News
Blog
Contact Us

 1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
 High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
 High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
 Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
 Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis
Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis