Top 10 Tips for Using a Battery Discharge Tester Effectively
When it comes to maintaining the health and performance of your batteries, the use of a Battery Discharge Tester is an essential practice for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. This invaluable tool helps you accurately assess the state of your battery by simulating a real-world discharge scenario. With the right approach, you can avoid unexpected battery failures and prolong the lifespan of your devices. However, to fully harness the potential of a Battery Discharge Tester, one must be familiar with the best practices that enhance its effectiveness.
In this guide, we will explore the top tips for using a Battery Discharge Tester efficiently. Whether you’re testing batteries for automotive applications, deep-cycle batteries, or portable electronics, implementing these strategies will ensure precise readings and reliable results. Understanding the nuances of proper usage can significantly impact your battery management routine, leading to improved performance and safety. Let’s delve into the key points that will aid you in becoming proficient with your Battery Discharge Tester and ensure optimal battery care.

Understanding Battery Discharge Testers and Their Importance in Maintenance
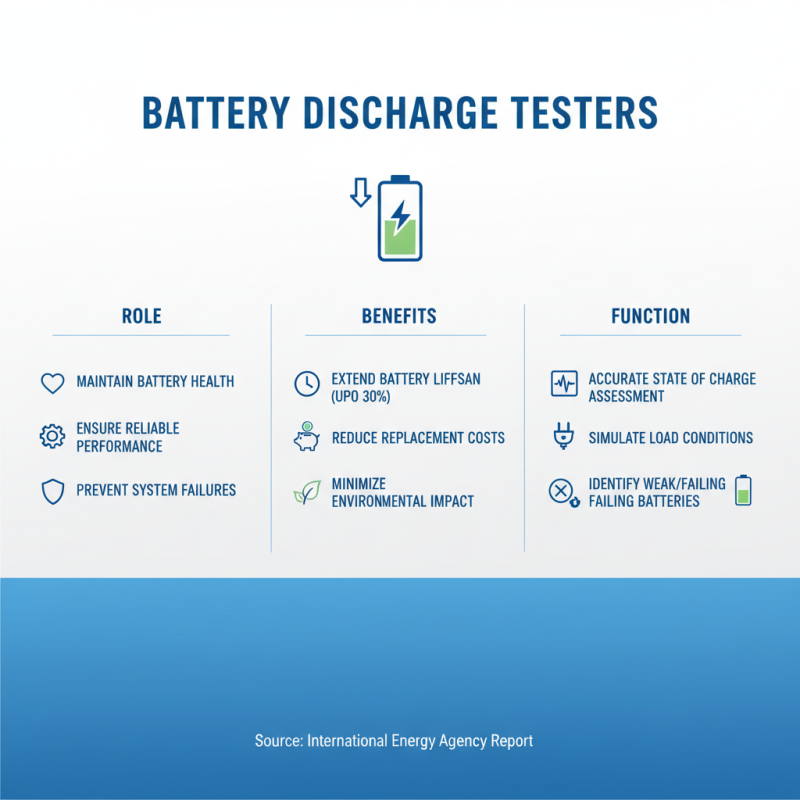
Battery discharge testers play a crucial role in maintaining battery health and ensuring reliable performance in various applications, from automotive to industrial systems. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, proper battery maintenance can extend the lifespan of batteries by up to 30%, significantly reducing replacement costs and minimizing environmental impact. These devices provide an accurate assessment of a battery's state of charge and overall condition by simulating load conditions. This allows users to identify weak or failing batteries before they can cause system failures or unsafe situations.
Regular testing with a battery discharge tester not only enhances safety but also supports operational efficiency. According to the Battery Council International, approximately 25-30% of batteries in service may be underperforming, leading to increased energy consumption and operational downtime. By integrating discharge testing into routine maintenance schedules, businesses can ensure optimal battery performance. This proactive approach not only boosts reliability but also contributes to sustainability efforts by reducing waste associated with premature battery disposal. Proper understanding and utilization of battery discharge testers are essential for any maintenance strategy focused on longevity and efficiency.
Key Parameters to Measure During Battery Discharge Testing
When conducting battery discharge testing, measuring key parameters is crucial to assessing performance and longevity. One of the primary parameters to evaluate is the discharge rate, typically expressed in amperes. The discharge rate directly influences how quickly a battery can deliver its stored energy. Research indicates that a higher discharge rate can lead to increased temperatures within the battery, affecting its capacity and potentially shortening its life. Additionally, adhering to recommended discharge rates based on the battery type is essential, as various chemistries operate optimally under specific conditions.
Another critical parameter is the end-of-discharge voltage (EDV), which indicates when a battery should be retired from service to avoid damage and degradation. Most batteries have a threshold voltage that, when reached, signifies the completion of their usable life cycle. According to industry reports, consistently discharging a lead-acid battery below 10.5V can result in irreversible damage, while lithium-ion batteries typically have a lower threshold of around 3.0V per cell. Monitoring this field during testing not only helps in maintaining battery health but also optimizes the cost-effectiveness of battery usage.
Temperature during the discharge cycle also plays a notable role in the performance metrics of batteries. Elevated temperatures can lead to thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries, while lower temperatures can exacerbate internal resistance in lead-acid batteries. A recent report from the Battery University highlights that maintaining an optimal temperature range of 20°C to 25°C is beneficial for maximizing battery efficiency. By meticulously tracking these parameters—discharge rate, end-of-discharge voltage, and temperature—users can effectively utilize a battery discharge tester and prolong the lifespan of their batteries.
Top 10 Tips for Using a Battery Discharge Tester Effectively - Key Parameters to Measure During Battery Discharge Testing
| Tip No. |
Key Parameter |
Measurement Unit |
Recommended Value |
Notes |
| 1 |
Voltage |
Volts (V) |
12.6 V for full charge |
Check before testing |
| 2 |
Current |
Amperes (A) |
0.5 C or as per specs |
Monitor during discharge |
| 3 |
Internal Resistance |
Ohms (Ω) |
Less than 10 mΩ |
Higher values indicate aging |
| 4 |
Temperature |
Celsius (°C) |
20-25 °C |
Affects performance |
| 5 |
Discharge Time |
Hours (h) |
Varies by capacity |
Track for consistency |
| 6 |
Capacity |
Amp-hours (Ah) |
50 Ah or as specified |
Check against rated capacity |
| 7 |
State of Charge |
Percentage (%) |
< 20% for testing |
Ideal for accurate results |
| 8 |
Load Test |
Amperes (A) |
50% of C-rate |
Simulate real-world usage |
| 9 |
End Voltage |
Volts (V) |
10.5 V (for lead-acid) |
Avoid excessive discharge |
| 10 |
Safety Precautions |
N/A |
Always follow guidelines |
Protect against accidents |
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Accurate Discharge Tests
When performing accurate battery discharge tests, it's crucial to follow a structured approach to ensure reliable results. Start by fully charging the battery to its optimal capacity, as this sets a clear baseline for the test. Use a battery discharge tester that meets the specifications of the battery type you are testing—whether it’s lead-acid, lithium-ion, or another kind. According to a report from the International Battery Association, a well-calibrated tester can help improve test accuracy by up to 15%.
Once the setup is complete, connect the tester securely, ensuring that all connections are tight and free from corrosion. Monitor the discharge process closely; it’s essential to record voltage and current at regular intervals. This practice not only provides insight into the battery's performance but also helps identify potential issues like capacity loss or irregular discharge patterns. Implementing efficient data logging practices can simplify analysis, allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of battery health.
While testing, it's also vital to maintain a controlled temperature environment, ideally between 20°C and 25°C, as extreme temperature fluctuations can adversely affect battery performance. You may want to refer to industry standards, such as those set by the Battery Council International, which highlight the importance of environmental factors in ensuring accurate testing results. By adhering to these tips and conducting thorough tests, you can maximize the reliability of your findings, promoting better battery management practices.
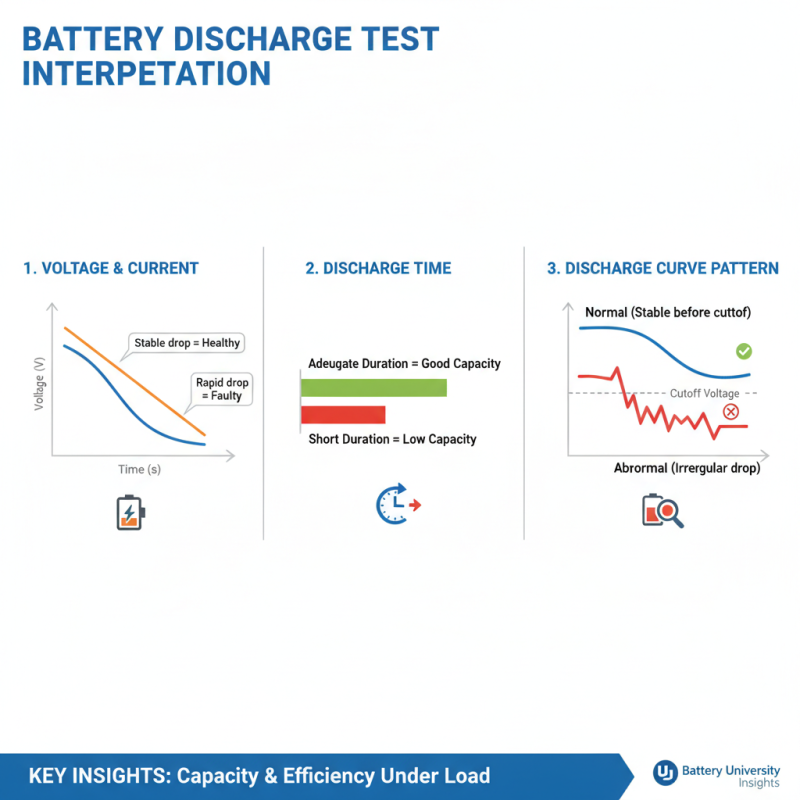
Interpreting Discharge Test Results: What the Data Reveals
Interpreting the results of a battery discharge test is crucial for understanding the health and performance of batteries. When a discharge test is conducted, various parameters such as voltage, current, and discharge time are measured. These figures reveal the capacity and efficiency of the battery under load conditions. For example, according to a recent industry report by the Battery University, a properly functioning battery typically exhibits a discharge curve that stabilizes before reaching a cutoff voltage, indicating adequate capacity retention. Deviations from this pattern could signify underlying faults, necessitating immediate attention.
Data from the International Battery Association indicates that improperly interpreted test results can lead to misinformed decisions regarding battery replacement or maintenance. A drop in voltage during the latter stages of a discharge test may suggest internal resistance is increasing, potentially due to age or contamination within the battery. Similarly, a quicker than expected drop in capacity can indicate issues with the battery chemistry. Understanding these nuances allows technicians to make better-informed decisions and can significantly extend battery life, ultimately saving costs and enhancing performance in applications ranging from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
Best Practices for Maintaining and Calibrating Your Discharge Tester
To ensure optimal performance of your battery discharge tester, regular maintenance and calibration are paramount. Start by keeping the device clean and free from dust or corrosion, which can affect its accuracy. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to wipe down connectors and terminals after each use. Additionally, inspect the cables for any signs of wear, as damaged cables can lead to inconsistent readings.
Calibration is another crucial aspect of maintaining your discharge tester. Regularly check its accuracy by testing against a known standard or reference battery. This practice not only ensures that your tester provides reliable data but also extends its lifespan. If discrepancies are found, adjust the settings according to the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult a professional for recalibration.
To make the most out of your discharge tester, always follow best practices during testing. For instance, fully charge the battery before testing to get accurate results. Run tests under stable temperature conditions, as extreme temperatures can skew your readings. Finally, keep detailed records of each test, including the date, battery type, and results, which will help track performance trends over time.

Home
Products
Power Cell Testing System
Digital Battery Testing System
 32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
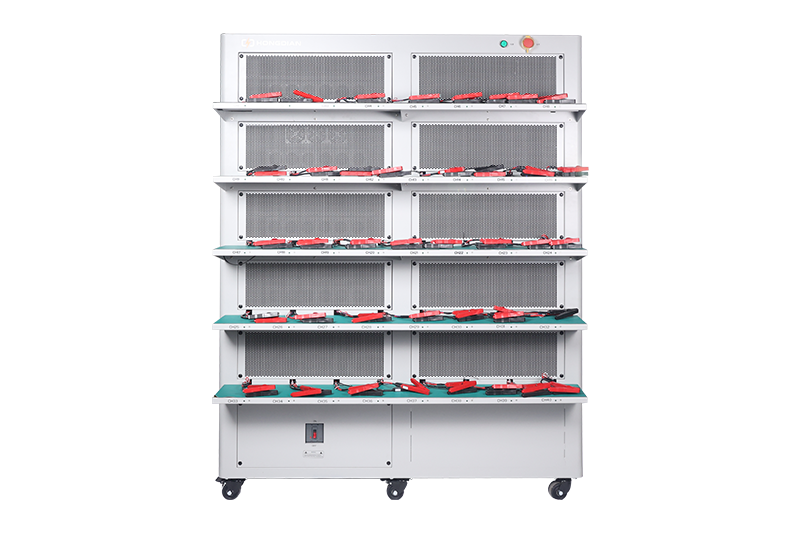 40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
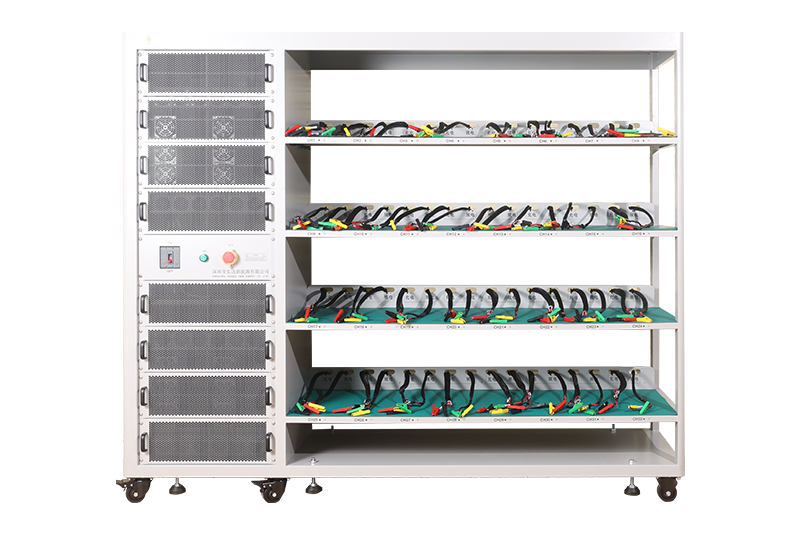 64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
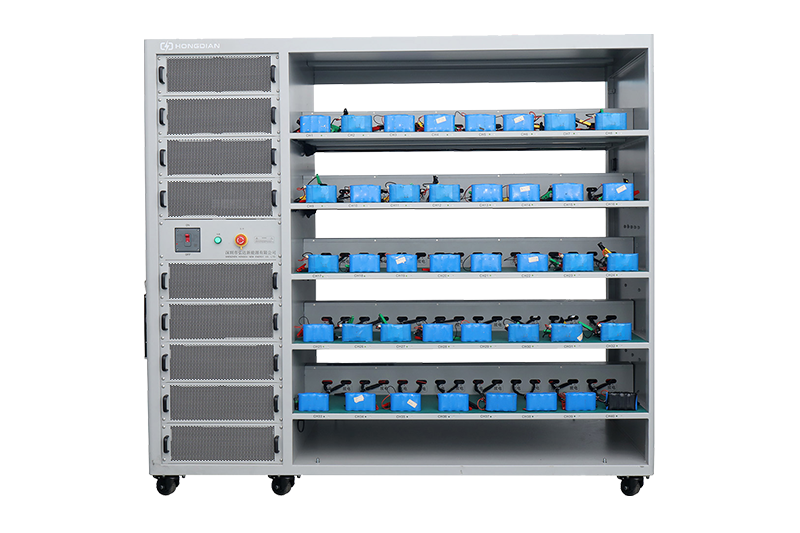 80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
Module Pack Testing System
Developing Portable Battery Testing
About Us
Service
Case&Solution
News
Blog
Contact Us

 1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
 High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
 High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
 Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
 Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis
Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis