How to Perform Effective Testing of Lead Acid Battery for Optimal Performance
Testing of lead acid batteries is a crucial process that ensures optimal performance and longevity of this widely used energy storage solution. As lead acid batteries are commonly found in various applications, from automotive to renewable energy systems, performing effective testing is essential to maintain their efficiency and reliability. This introductory outline aims to provide insights into the different methodologies and best practices involved in the testing of lead acid batteries, emphasizing their significance in improving battery life and operational efficacy.
In a world increasingly reliant on uninterrupted power supply, the demand for well-functioning lead acid batteries is ever-growing. Understanding the different aspects of testing—such as voltage, capacity, and internal resistance—can help identify potential issues before they lead to complete failure. Moreover, regular testing not only aids in maintaining peak performance levels but also helps in making informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacement. By exploring the fundamentals of battery testing and the tools required, individuals and organizations can ensure they are maximizing the potential of their lead acid batteries while reducing downtime and costs associated with unexpected failures.
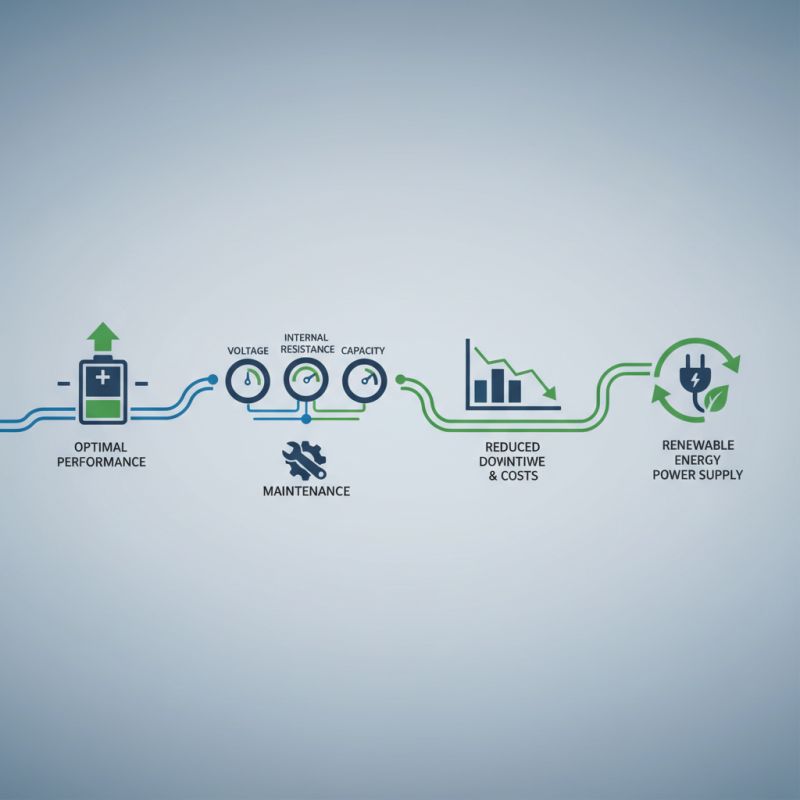
Understanding Lead Acid Battery Basics and Specifications
Understanding the basics and specifications of lead acid batteries is crucial for their optimal performance.
Lead acid batteries are composed of lead dioxide and sponge lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid.
They are widely recognized for their robustness and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for various applications,
from automotive to renewable energy systems. However, it's essential to know the different types, such as flooded, sealed, and gel,
as their specifications can significantly influence performance and lifespan.
To ensure effective testing of lead acid batteries, it's vital to measure key specifications like voltage, capacity, and internal resistance.
A multimeter can help you assess the battery's voltage under load and no load,
which provides insights into its health. Additionally, performing a load test will determine if the battery can sustain its rated capacity.
Tips: When testing, always check the battery's state of charge
before conducting tests to avoid misleading results. Keep your testing equipment calibrated for accuracy,
and remember to wear protective gear when handling batteries to ensure safety.
Regular monitoring and maintenance can enhance the longevity of lead acid batteries and help identify any issues early on.
Essential Tools Required for Testing Lead Acid Batteries
When testing lead acid batteries, having the right tools is crucial for accurate assessments and optimal performance. One of the most essential tools is a multimeter, which measures voltage and can help ascertain the battery's overall health. A good multimeter will allow you to quickly check the battery's state of charge and detect any issues with voltage levels that may indicate a failing battery. Additionally, a hydrometer is vital for testing the specific gravity of the electrolyte solution. This tool enables you to evaluate the state of charge more finely and identify any cells that may be underperforming.
Another important tool is a load tester, designed specifically for batteries. This device applies a simulated load to the battery while measuring its performance. This test helps determine how well the battery can deliver sustained power and can reveal any weaknesses that might not be apparent during a simple voltage check. Furthermore, using safety goggles and gloves is recommended, as they protect you from potential acid splashes or hazardous reactions while handling the battery. By ensuring you have the proper tools and safety equipment, you can perform effective testing on lead acid batteries, contributing to their longevity and reliable performance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Voltage and Capacity
To effectively assess the performance of a lead acid battery, testing its voltage and capacity is essential. Begin by ensuring the battery is fully charged and has rested for a few hours to allow the voltage to stabilize. Using a multimeter, measure the voltage across the terminals. A healthy, fully charged lead acid battery should typically read between 12.6 to 12.8 volts. If the reading falls below 12.4 volts, the battery may be undercharged or experiencing issues. Document these readings for future reference and comparison.
Next, to check the capacity, a more comprehensive test is required. This involves discharging the battery at a specified load until it reaches a certain voltage threshold, usually around 10.5 volts for lead acid batteries. During this discharge, it's crucial to monitor the voltage at regular intervals to determine how long the battery can sustain a load. Once the test is complete, compare the actual capacity with the rated capacity to evaluate how well the battery performs. A significant discrepancy may indicate degradation or a need for replacement. Regular testing will not only help in maintaining optimal performance but also prolong the battery's lifespan.
Analyzing Battery Performance Through Load Testing
Load testing is an essential method for analyzing the performance of lead-acid batteries. This process involves applying a specific load to the battery while monitoring its voltage and current output. The primary goal is to simulate real-world usage conditions, allowing testers to assess how well the battery can handle demands during operation. A decline in voltage under load can indicate potential issues, such as sulfation or internal resistance, which might compromise the battery's overall performance.
When performing load testing, it is vital to follow a clear set of guidelines to ensure accurate results. **Tips:** First, ensure the battery is fully charged before starting the test. A discharge that begins from a fully charged state captures a more reliable representation of the battery's performance. Secondly, use a load tester that matches the battery's specifications, typically applying a load equal to half of its cold cranking amps (CCA) rating for about 15 seconds. Finally, monitor the voltage drop closely; a significant drop below the manufacturer’s recommended level can signal that the battery needs maintenance or replacement.
In addition to load testing, it's wise to conduct regular checks on the battery's fluid levels and electrolyte density. **Tips:** Top off the fluid with distilled water if necessary, and utilize a hydrometer to measure the specific gravity of the electrolyte. These practices help maintain optimal performance and extend the battery's lifecycle, ensuring reliability when you need it most.
How to Perform Effective Testing of Lead Acid Battery for Optimal Performance - Analyzing Battery Performance Through Load Testing
| Test Parameter |
Value |
Unit |
| Voltage (Fully Charged) |
12.6 |
Volts |
| Voltage (Under Load) |
11.8 |
Volts |
| Load Current |
100 |
Amperes |
| Battery Temperature |
25 |
°C |
| Internal Resistance |
0.005 |
Ohms |
| Capacity Test Result |
120 |
Ah (Amp hours) |
| Cycle Life |
500 |
Cycles |
| Discharge Rate |
0.2 |
C (Capacity) |
Interpreting Test Results for Optimal Battery Maintenance
Interpreting test results for lead acid batteries is crucial for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. When conducting tests, key parameters such as voltage, specific gravity, and internal resistance should be meticulously analyzed. A fully charged lead acid battery typically operates at around 12.6 volts or higher. If the voltage drops significantly, it may indicate that the battery is not holding a charge, necessitating further investigation. Additionally, measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte can provide insights into the state of charge; readings below 1.200 suggest that the battery may need recharging.
Understanding these metrics allows for timely maintenance actions. For instance, a battery showing low specific gravity can benefit from equalization charging, a process that balances the charge across all cells. Furthermore, monitoring internal resistance is essential; not only does it help in diagnosing potential issues, but it also indicates the battery’s overall health. A rise in resistance may suggest sulfation or degradation, indicating that preventive measures or even replacement might be needed. By carefully interpreting these test results, users can ensure that their lead acid batteries are maintained in peak condition, maximizing both performance and lifespan.

Home
Products
Power Cell Testing System
Digital Battery Testing System
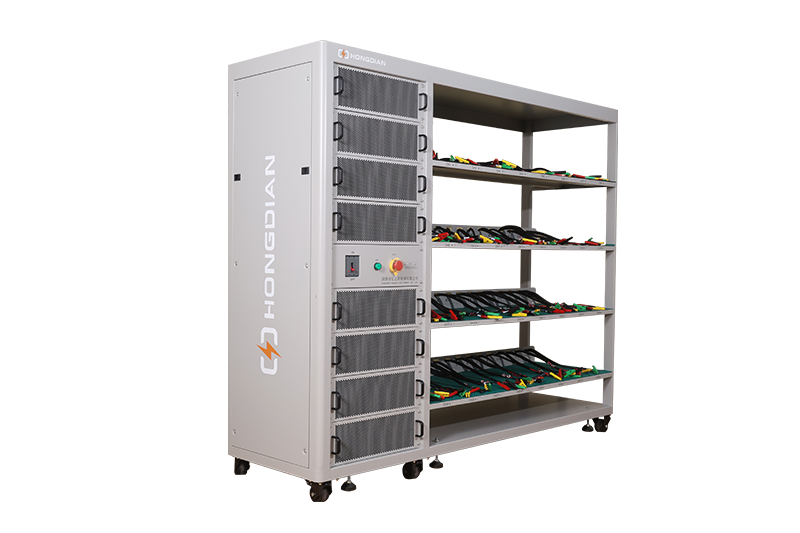 32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
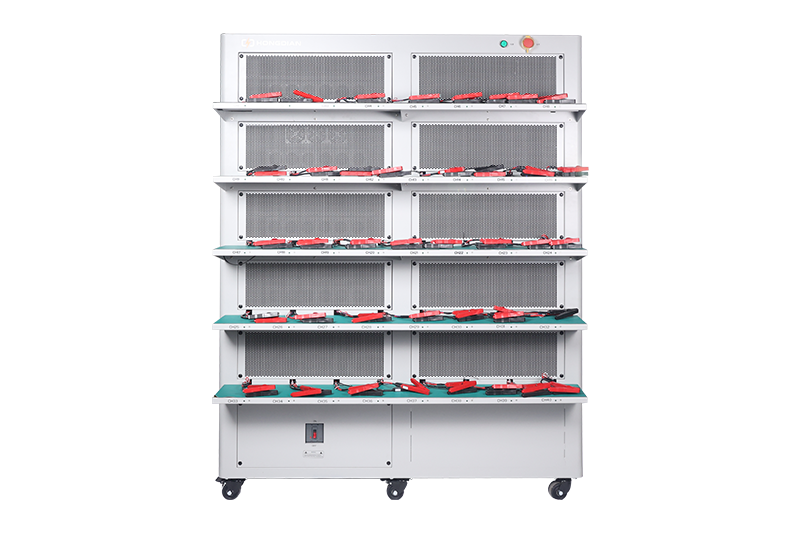 40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
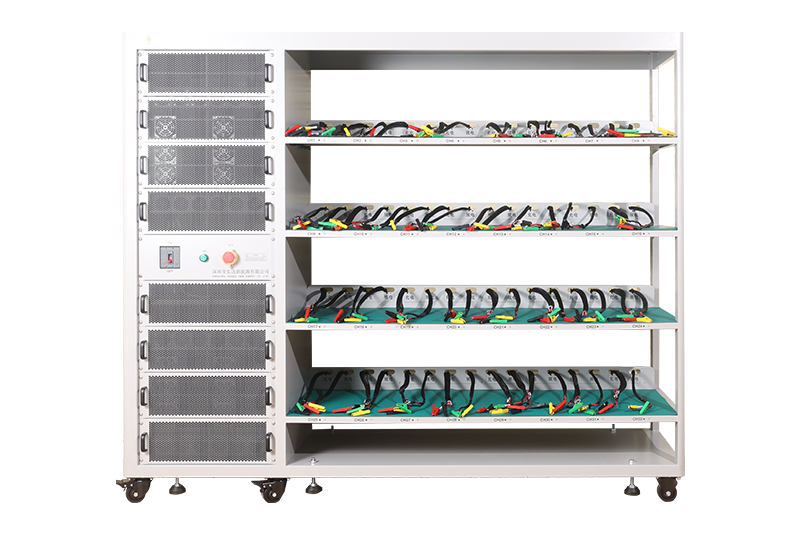 64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
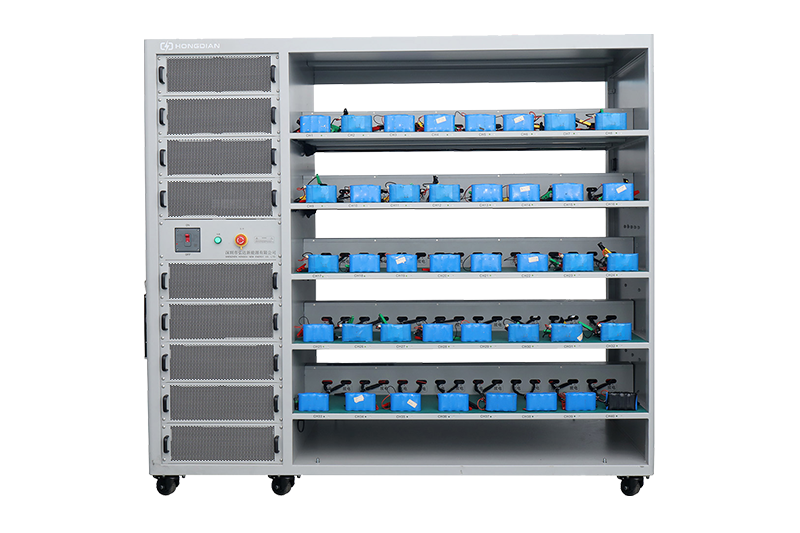 80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
Module Pack Testing System
Developing Portable Battery Testing
About Us
Service
Case&Solution
News
Blog
Contact Us

 1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
 High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
 High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
 Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
 Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis
Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis








