2025 How to Choose and Use a Rechargeable Battery Tester for Optimal Performance
In an age where sustainable energy solutions are paramount, understanding the optimal use of rechargeable batteries has become essential. The efficiency and longevity of these batteries largely depend on their proper maintenance and testing.
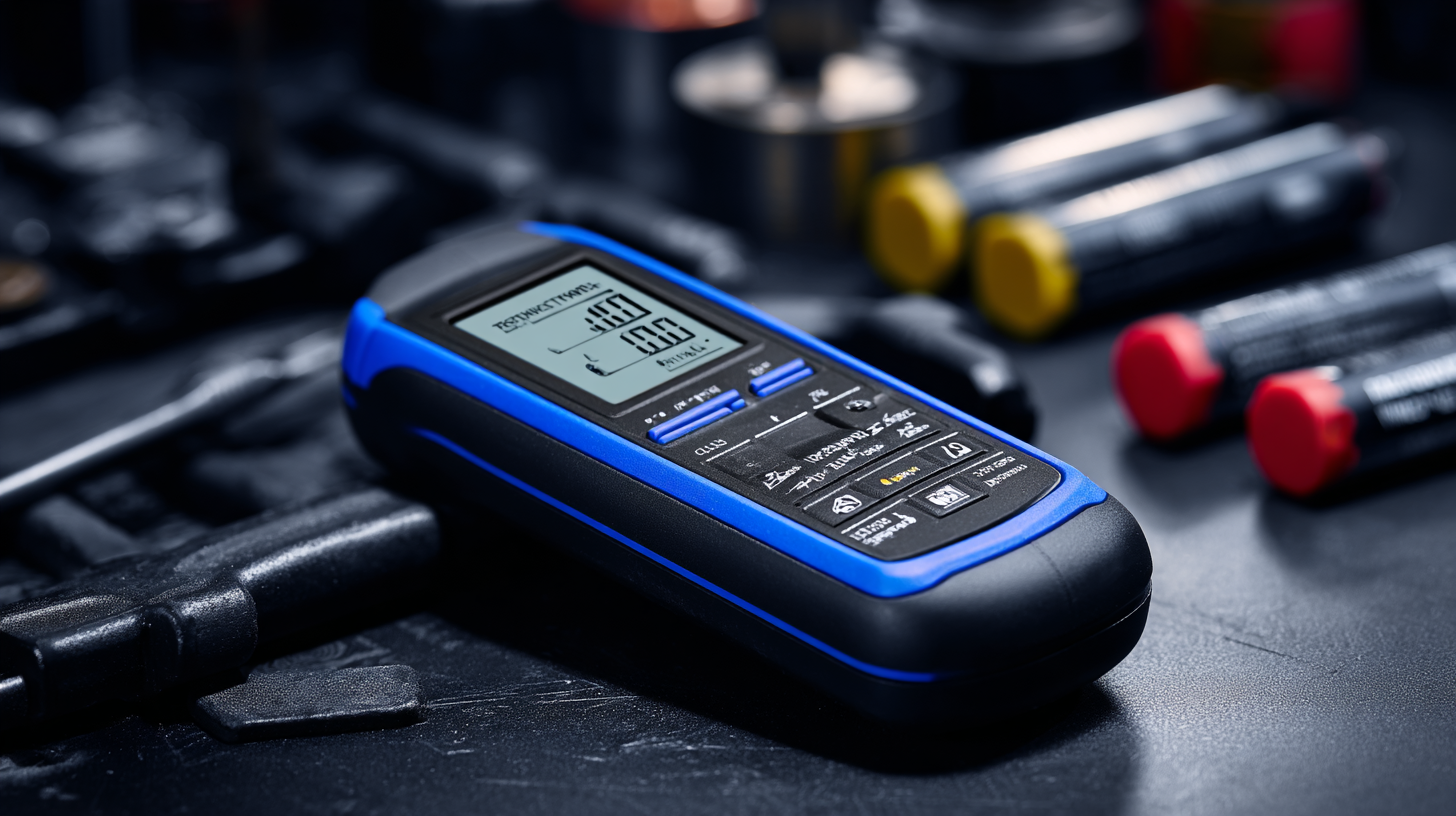 Enter the Rechargeable Battery Tester, an invaluable tool for both casual users and dedicated enthusiasts. This device ensures you can keep track of your batteries' performance, helping you to ascertain their charge levels, remaining capacity, and overall health.
Enter the Rechargeable Battery Tester, an invaluable tool for both casual users and dedicated enthusiasts. This device ensures you can keep track of your batteries' performance, helping you to ascertain their charge levels, remaining capacity, and overall health.
Choosing the right rechargeable battery tester can make all the difference in achieving peak performance from your batteries. With so many options available on the market, navigating the various features and specifications can be daunting. In this guide, we will explore key considerations for selecting the appropriate tester and provide helpful tips for its effective use.
By understanding the functionality of a rechargeable battery tester, you can maximize the life and efficiency of your rechargeable batteries, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Understanding Different Types of Rechargeable Battery Testers Available in 2025
In 2025, the market offers a diverse range of rechargeable battery testers, each designed to cater to various battery types such as NiMH, Li-ion, and Lead-acid. Understanding the differences in these testers can significantly enhance user experience and ensure optimal performance. According to a study by ResearchAndMarkets, the global demand for battery testers is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% through 2027, underscoring the increasing importance of choosing the right device for battery maintenance.
When selecting a rechargeable battery tester, consider the compatibility with specific battery chemistries. For instance, some testers are optimized for NiMH batteries, offering accurate readings on their voltage levels and remaining capacity, while others may be better suited for Lithium-ion batteries, which require precise measurements due to their sensitivity to charge levels.
**Tips:** Always look for testers that provide a digital display for ease of reading and those that come with built-in safety features to prevent over-testing. Additionally, consider a model that includes data logging capabilities, as this can help track the performance of multiple batteries over time, ultimately enhancing their lifecycle.
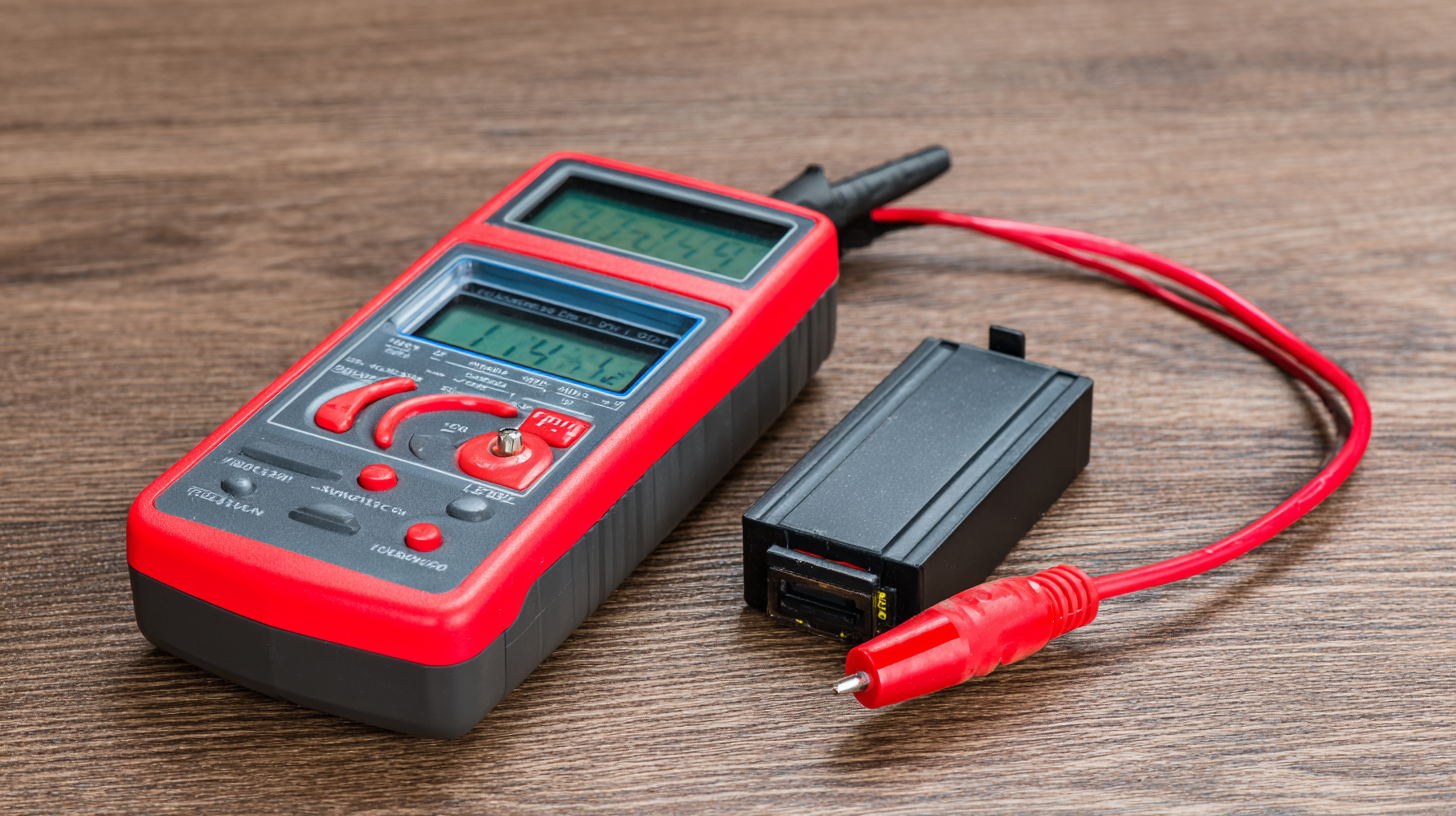

Key Features to Look for When Selecting a Rechargeable Battery Tester
When selecting a rechargeable battery tester, there are several key features to consider to ensure optimal performance. First, look for testers that can handle various battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and nickel-cadmium (NiCd). According to a report by the Battery University, lithium-ion batteries are projected to dominate the market, accounting for nearly 75% of global battery sales by 2025. Therefore, a versatile tester that performs well with these batteries is essential.
Another crucial feature is the tester's accuracy and range in measuring voltage and capacity. A 2021 study by the International Energy Agency highlights that incorrect readings can lead to poor battery maintenance and efficiency losses of up to 30%. Select testers that provide precise measurements for both voltage and current, ensuring they can identify the health status of your batteries. Additionally, look for testers with user-friendly interfaces and clear readouts, as convenience can significantly enhance your battery management experience. By prioritizing these features, users can effectively extend battery life and maintain optimal performance.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Use a Rechargeable Battery Tester Effectively
Using a rechargeable battery tester effectively requires a clear understanding of both the device and the batteries you intend to test. Begin by reading the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific tester model, as features can vary. Ensure that the tester is fully charged or has fresh batteries, as this will influence its accuracy. Start by selecting the appropriate setting on the tester that corresponds to the type of battery you are evaluating—this may include options for various chemistries such as NiMH, Li-ion, or lead-acid.
Once the tester is prepared, carefully insert the rechargeable battery into the designated slot, ensuring proper contact with the test probes. Many testers will display a clear reading of the battery's voltage and overall health. For optimal use, compare the displayed values against the battery specifications; understanding the acceptable voltage range is crucial for determining whether the battery is performing well or needs to be recharged or replaced. Regular testing, especially before relying on batteries for critical devices, can prevent unexpected failures and extend the lifespan of your rechargeable batteries.
Tips for Maintaining Your Rechargeable Battery Tester for Long-Term Use
To ensure the longevity and reliability of your rechargeable battery tester, regular maintenance is essential. First, keep the tester clean by wiping it down with a soft cloth after each use to remove dust, battery residue, and other contaminants. Avoid using harsh chemicals that might damage the testing surfaces. Additionally, store the tester in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent moisture-related issues that can impair its functionality.
Another important aspect of maintaining your battery tester is checking its calibration periodically. Over time, the readings may become inaccurate, leading to improper battery assessments. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines to recalibrate your tester as needed. Furthermore, always use fresh batteries in the tester to avoid low power that can skew results. By paying attention to these maintenance tips, you can ensure that your rechargeable battery tester remains an effective tool for assessing battery health and performance over the years.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Testing Rechargeable Batteries in 2025
When testing rechargeable batteries in 2025, it's crucial to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccuracies and suboptimal performance. One significant pitfall is neglecting to use a proper battery tester designed for the specific chemistry of the batteries being tested. For example, many users mistakenly utilize generic testers, which may not provide precise readings for lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in devices today. By using a tester tailored for the battery type, users can receive accurate voltage and capacity assessments, leading to better decision-making regarding battery health and lifespan.
Another frequent error is failing to consider the state of charge before testing. A battery’s state of charge can significantly influence test results, making it appear to be in better or worse condition than it actually is. Experts recommend fully charging the battery before testing to ensure the readings reflect its true capacity and performance potential. Additionally, many consumers overlook the importance of ambient temperature; tests conducted in extremes of heat or cold can yield misleading results. Keeping these factors in mind will enhance the effectiveness of battery testing, ultimately prolonging the life of your rechargeable options.
2025 How to Choose and Use a Rechargeable Battery Tester for Optimal Performance - Common Mistakes to Avoid When Testing Rechargeable Batteries in 2025
| Testing Parameter |
Recommended Value |
Common Mistakes |
| Voltage |
3.7V for Lithium-ion |
Not testing under load |
| Capacity Check |
2000mAh for typical AA |
Ignoring temperature effects |
| Internal Resistance |
< 30mΩ for high-performance |
Not calibrating tester |
| Charge Cycles |
300+ for NiMH |
Failing to monitor cycles |
| Self-Discharge Rate |
< 20% per month |
Using old batteries for testing |

Home
Products
Power Cell Testing System
Digital Battery Testing System
 32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
32/48 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
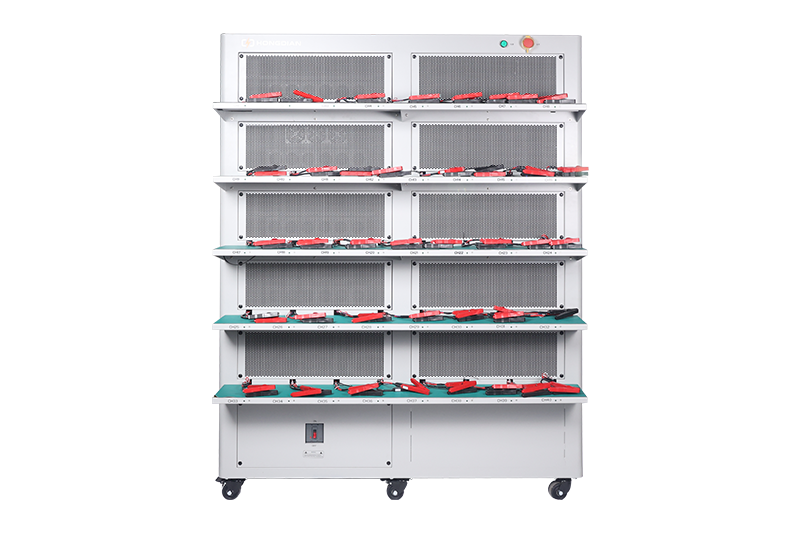 40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
40 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
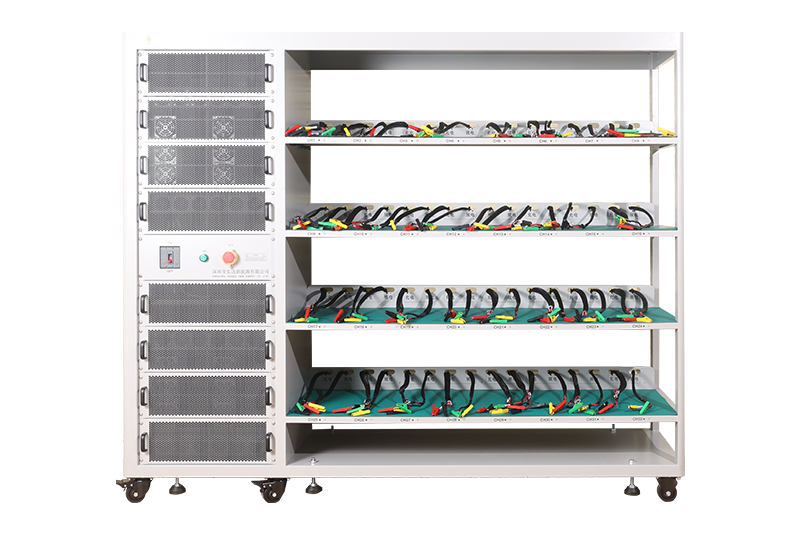 64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
64 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
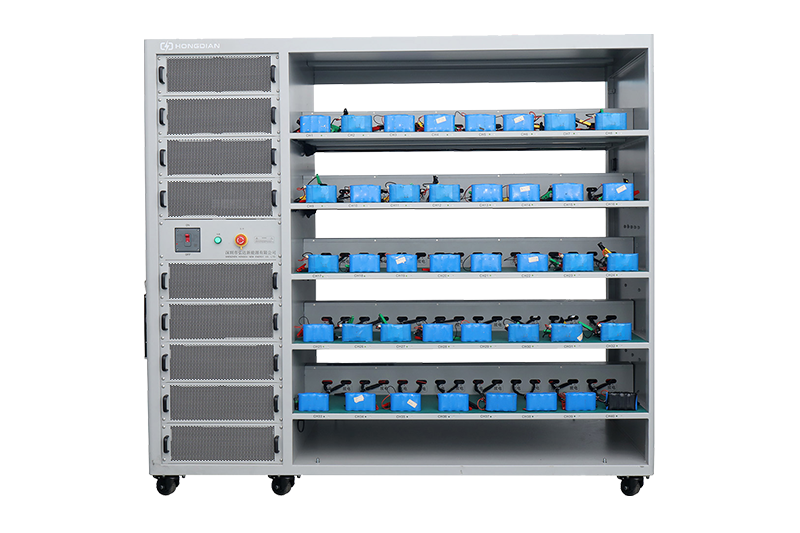 80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
80 channel battery charging and discharging test integrated battery cabinet
Module Pack Testing System
Developing Portable Battery Testing
About Us
Service
Case&Solution
News
Blog
Contact Us

 1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
1000V-1500V High Voltage High Current Battery Testing System
 High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
High-Precision Battery Testing System for Enhanced Performance Monitoring 30V/60V/100V/120V
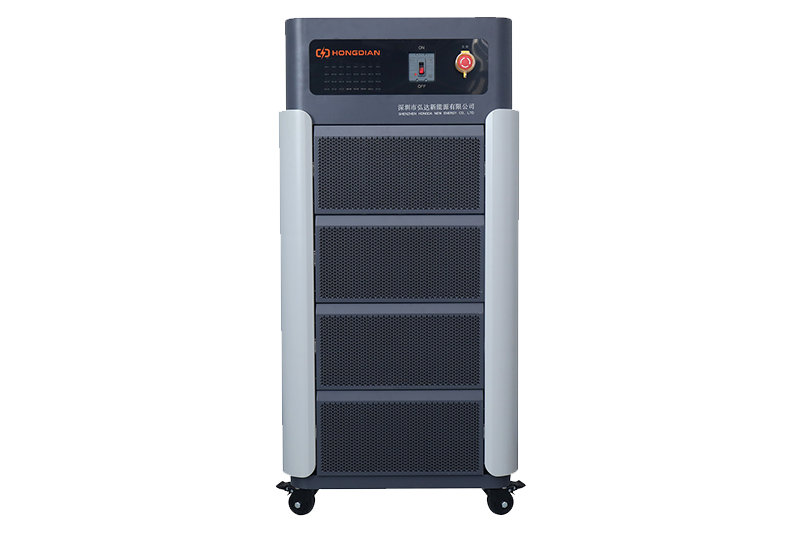 High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
High-Precision Battery Charge Discharge Test Systems for EV Manufacturers
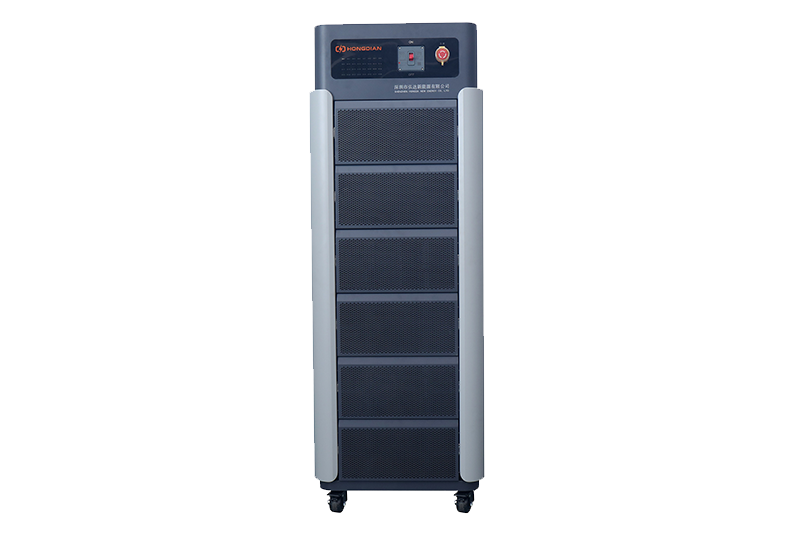 Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
Precision Battery Test Racks for Cell Capacity & Internal Resistance Measurement
 Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis
Multi-Channel Battery Testing Equipment for Parallel Performance Analysis
 Enter the Rechargeable Battery Tester, an invaluable tool for both casual users and dedicated enthusiasts. This device ensures you can keep track of your batteries' performance, helping you to ascertain their charge levels, remaining capacity, and overall health.
Enter the Rechargeable Battery Tester, an invaluable tool for both casual users and dedicated enthusiasts. This device ensures you can keep track of your batteries' performance, helping you to ascertain their charge levels, remaining capacity, and overall health.


